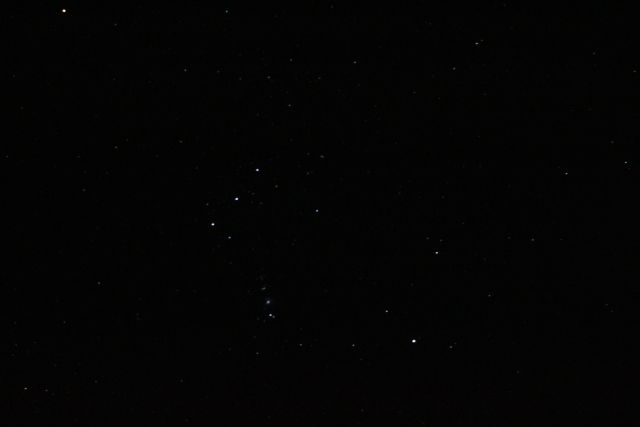




























O --- singly ionized helium (HeII) in emission or absorption
B --- neutral helium (HeI) lines in absorption
A --- neutral hydrogen (HI) lines in absorption
F --- once ionized calcium (CaII) lines in absorption
G --- neutral metallic lines and once ionized calcium (CaII) lines in absorption
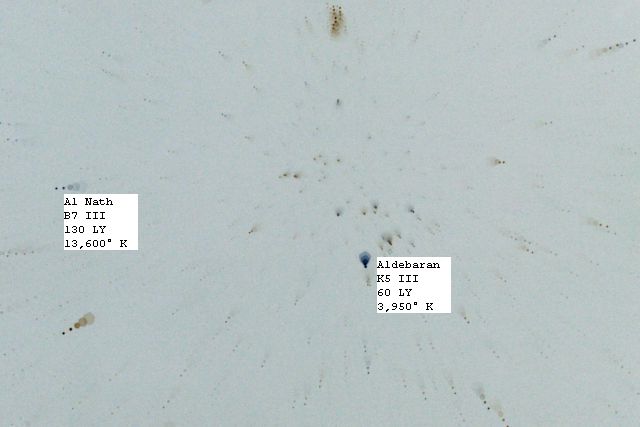
K --- metallic lines in absorption
M --- some molecular bands of TiO in absorption
O --- 28,000 - 50,000 degrees K (color: blue)
B --- 9,900 - 28,000 degrees K (color: bluish white)
A --- 7,400 - 9,900 degrees K (color: white)
F --- 6,000 - 7,400 degrees K (color: yellowish white)
G --- 4,900 - 6,000 degrees K (color: yellow)
K --- 3,600 - 4,900 degrees K (color: orange)
M --- 2,000 - 3,600 degrees K (color: red)
C-R --- 2,800 - 5,100 degrees K (carbon star of G/K) (color: deep red)
C-N --- 2,600 - 3,100 degrees K (carbon star of K/M) (color: deep red)
Ia --- Bright supergiants
Ib --- Supergiants
II --- Bright Giants
III --- Giants
IV --- Sub Giants
V --- Main Sequence
VI --- Sub dwarfs
VII --- White dwarfs
e --- Emission line star
em --- Emission by metal lines
ep --- Pecular emission
eq --- P Cygni emission
er --- Reversed emission
f --- Helium and Nitrogen emission
k --- Interstellar lines
m --- Strong metallic absorption
n --- Nebulous diffuse lines
nn --- Very diffuse lines
p --- Chemically pecular spectrum
s --- Sharp lines
si --- Silicon star
v --- Variation in spectrum
wk --- Weak lines